Introduction
As a large-scale purchaser in the home textile industry, it is crucial to have a deep understanding of the products you source. In this article, we will delve into the science behind memory foam, shedding light on its material composition and performance. By comprehending the intricacies of memory foam, you can make informed decisions that align with your customer’s needs and preferences.
What is Memory Foam?
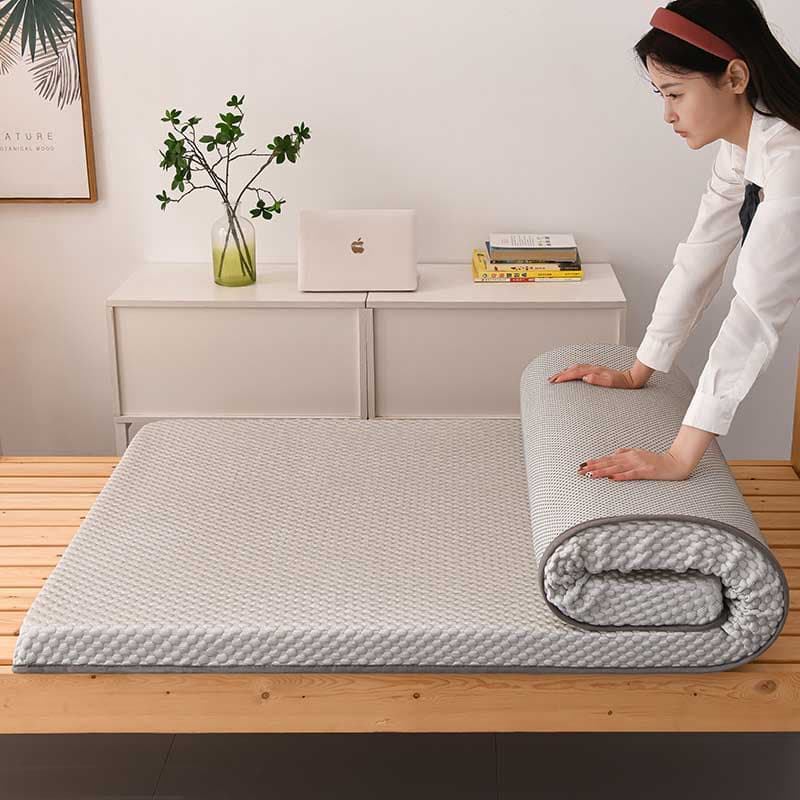
Memory foam is a viscoelastic material that responds to pressure and heat, conforming to the shape of an object and slowly returning to its original form when the pressure is removed. It was originally developed by NASA in the 1960s to improve seat cushioning and crash protection for astronauts.
Material Composition
Memory foam is primarily composed of polyurethane, a synthetic polymer. To enhance its viscoelastic properties, various additional chemicals and additives are incorporated during the manufacturing process. These additives can include temperature-sensitive substances, flame retardants, and antimicrobial agents, among others.
Viscoelastic Properties
The viscoelastic nature of memory foam is a key feature that distinguishes it from traditional cushioning materials. When pressure is applied, the foam deforms and distributes the load over a larger area. This property helps relieve pressure points, making memory foam an ideal choice for mattresses, pillows, and seating solutions.
Heat and Temperature Sensitivity
Memory foam is heat-sensitive, meaning it reacts to body heat. As the foam comes into contact with body heat, it softens and molds itself to the contours of the individual, providing personalized support. Temperature-sensitive memory foams are designed to adjust their firmness depending on the ambient temperature, offering optimal comfort throughout the year.
Performance Factors
a. Density: Memory foam is available in different densities, ranging from low to high. Higher-density foams are generally more durable and offer better support, while lower-density foams tend to be softer and more conforming.
b. Indentation Load Deflection (ILD): ILD measures the foam’s firmness and is determined by the force required to compress a sample by a certain percentage. Understanding ILD can help you select memory foam products with the desired level of support.
c. Recovery Time: The recovery time of memory foam refers to how quickly it returns to its original shape after pressure is released. Faster recovery times indicate a more responsive foam.
Certifications and Standards
When sourcing memory foam products, it is important to consider certifications such as CertiPUR-US® and Oeko-Tex® Standard 100. These certifications ensure that the foam meets rigorous quality, performance, and environmental standards.
Conclusion
Memory foam’s unique properties make it a popular choice in the home textile industry. By understanding the material composition and performance factors of memory foam, you can confidently select products that cater to your customers’ needs. Keep in mind density, ILD, recovery time, and certifications when making purchasing decisions. Stay informed and provide your customers with exceptional comfort and quality through the power of memory foam.